Strategic Integration: Data Science & Business Analytics in the Digital Era
In the modern AI and digital era, data science (DS) and business analytics (BA) are co-interconnected. This integration allows technical concepts to drive business processes, creating a foundation for global growth and competitive dominance. Data-driven companies are 10x to 20x more likely to outperform global competitors.
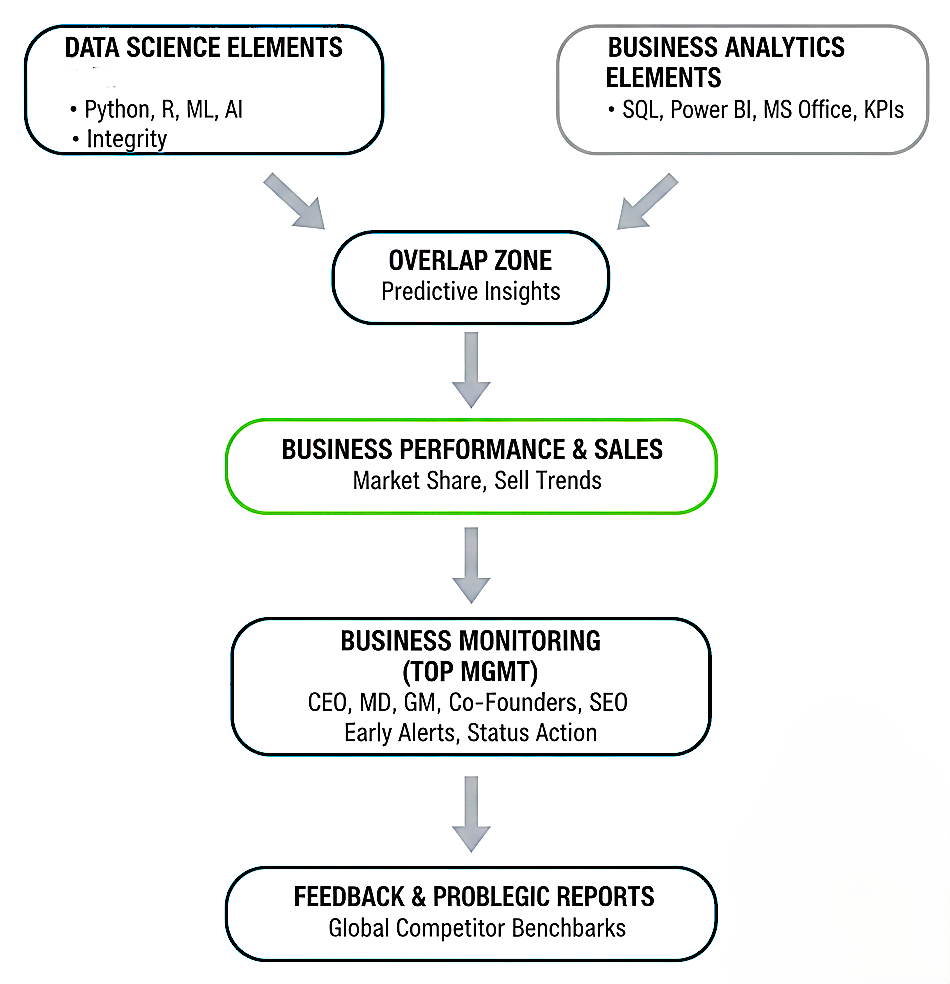
1. The Integrated Block Diagram (The Ecosystem)
This diagram illustrates the flow from data extraction to high-level strategic reporting.
[ DATA SCIENCE ELEMENTS ] [ BUSINESS ANALYTICS ELEMENTS ]
(Python, R, ML, AI, Integrity) (SQL, Power BI, MS Office, KPIs)
\ /
\____[ OVERLAP ZONE ]__________/
(Predictive Insights)
|
[ BUSINESS PERFORMANCE & SALES ]
(Market Share, Product Sell Trends)
|
v
[ BUSINESS MONITORING (TOP MGMT) ]
(CEO, MD, GM, Co-Founders, SEO)
|
v
[ FEEDBACK & PROBLEM SOLVING ]
(Early Alerts, Status Action)
|
v
[ FINAL STRATEGIC REPORTS ]
(Global Competitor Benchmarks)
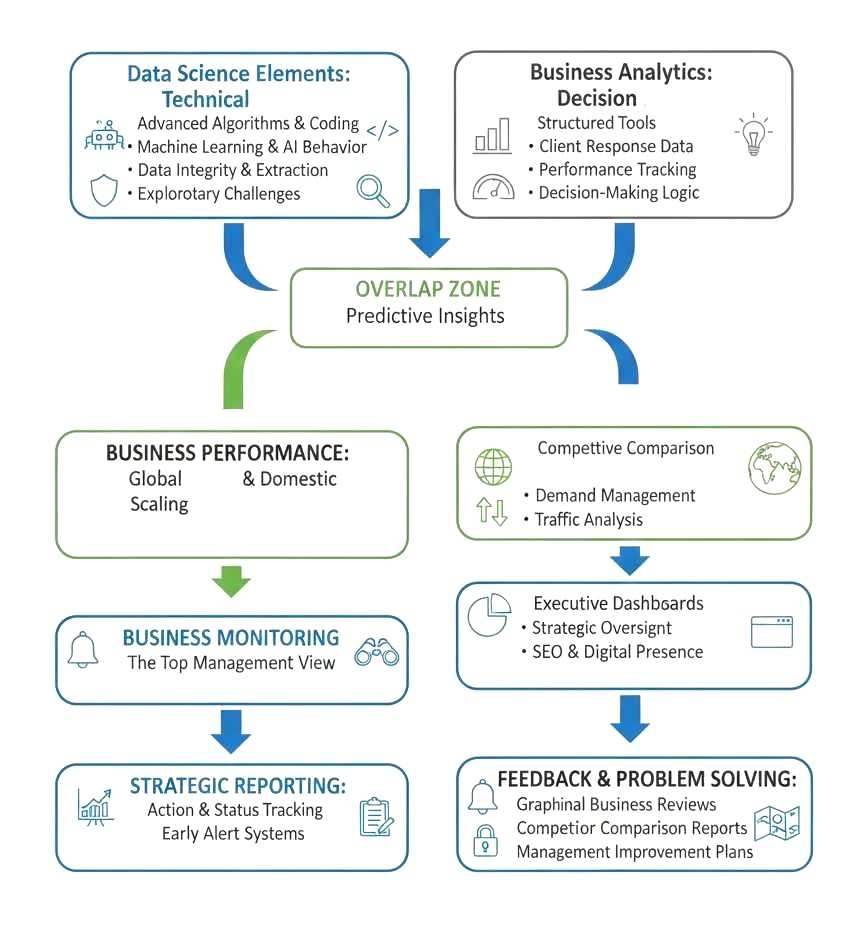
2. Data Science: Technical Elements
Data Science serves as the technical engine, extracting “inside” data through business console tools to build the foundation for all activities:
- Advanced Algorithms & Coding: Using Python and R to build models that discover deep insights into business structures.
- Machine Learning & AI Behavior: Automating the extraction of patterns from products and services data.
- Data Integrity & Extraction: Ensuring unstructured and structured data are clean and reliable across various industries Globally.
- Exploratory Challenges: Tackling complex, open-ended problems to build models for future trends.
3. Business Analytics Elements: Decision Drive
Business Analytics focuses on compiling data to drive specific outcomes and help make critical business decisions:
- Structured Tools: Utilizing SQL, MS Office, and Power BI to translate data into graphical business processes.
- Client Response Data: Solving specific problems by analyzing feedback and reporting domestic trends.
- Performance Tracking: Focusing on the “Business Sell” and department reviews to measure overall Status
- Decision-Making Logic: Converting technical depth into actionable business intelligence.
4. Business Performance: Global & Domestic Scaling
To meet global standards, companies must monitor market diversity and performance:
- Competitive Comparison: Using APIs to integrate latest global trends, news, and competitor price shifts.
- Demand Management: Controlling manufacturing and selling “up and down” trends based on real-time data.
- Traffic Analysis: Monitoring market diversity and traffic (e.g., from the USA and other countries) to prevent losses and optimize exports.
5. Business Monitoring: The Top Management View
This stage is critical for Investors, CEOs, MDs, GMs, and Co-founders to monitor the overall health of the organization:
- Executive Dashboards: High-level visualization of department performance and sales feedback.
- Strategic Oversight: Using the technical analysis background to manage business development.
- SEO & Digital Presence: Monitoring how the brand performs in the global digital market.
6. Feedback & Problem Solving: Early Alert Systems
Management must have a mechanism for immediate intervention:
- Early Alert Control: Using technical depth analysis to trigger alerts before business risks manifest.
- Action & Status Tracking: Real-time visibility into the “Problem Solving Action Status” of customer complaints or supply chain issues.
- Diversity Prevention: Imposing strategies to prevent “selling diversity” risks and protect global export interests.
7. Strategic Reporting: The Final Output
The end result of this cycle is the creation of professional reports that guide the company’s future:
- Graphical Business Reviews: Visual reports on sales, feedback, and department efficiency.
- Competitor Comparison Reports: A detailed look at how the company stands against global rivals.
- Management Improvement Plans: Data-driven roadmaps for business development and future investment.
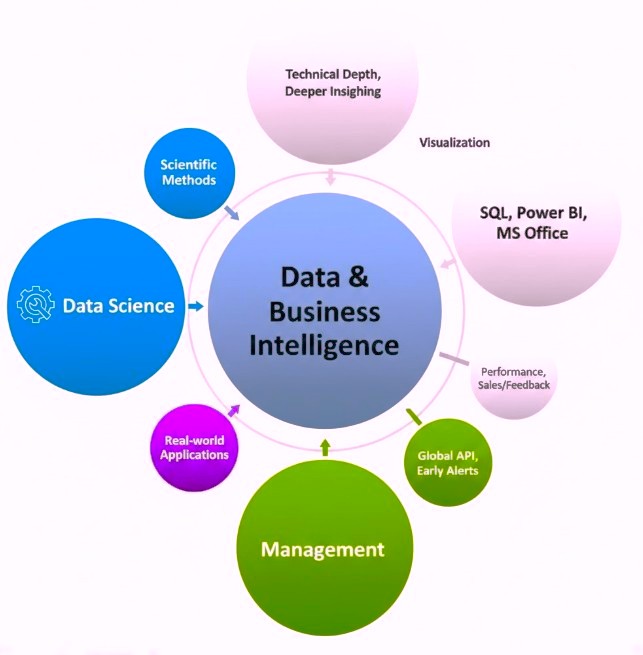
Summary of Requirements & Skills
| Category | Skills & Tools | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Data Science | Python, R, AI, ML, Data Integrity | Technical depth, Deeper insights, Model building. |
| Business Analytics | SQL, MS Office, Power BI, Decision Logic | Performance, Sales/Feedback, Decision support. |
| Management | Monitoring, Strategic Oversight, Global API | Early Alerts, Competitor dominance, Scaling. |
CONCLUSION:
To compete effectively on a global level and in the market, large companies are using data science and big analytics to gain a 360-degree, 24/7 view of their operations at every level, including sales, logistics, warehousing, products, scientific expertise, and employee performance.
According to a business founder, what steps should you take to leverage data science and big analytics technology to scale your large business?
How can you effectively use and implement data science and analytics technology to increase your business productivity by 4 to 10 times?
