Professional Workflow Automation
Advanced Tools & Strategies to Enhance Professional Skills
Workflow automation has become an essential skill for Modern professionals “force multiplier” increasing efficiency and enabling more strategic work. Mastering its core principles demonstrates technical agility and prepares you for the automation roadmap of 2026.
1. The Core Automation Pillars
A. AI Orchestration & Integration
These tools act as the “connective tissue” between disconnected SaaS applications.
- Zapier: The gold standard for no-code. Ideal for simple “If This, Then That” logic across 6,000+ apps.
- Make (formerly Integromat): Superior for multi-step workflows requiring complex data parsing and error handling.
- n8n: Highly customizable; allows you to host your own data and inject custom JavaScript nodes for maximum flexibility.
- Pipedream: Integration platform for developers that provides a low-code approach to connecting APIs.
B. Intelligent Knowledge Management
Automating how information is captured, organized, and retrieved.
- Notion: Uses AI to summarize meeting notes, generate action items, and maintain databases automatically.
- Obsidian: For professionals needing a local “Second Brain” with powerful community plugins for automated linking.
- Readwise: Automates the flow of highlights from books and articles directly into your writing workspace.
C. Specialized Skill & RPA Tools
Advanced tools for automating desktop tasks and web data extraction.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Deep integration with Excel macros and Teams approvals; essential for corporate environments.
- UiPath: The leader in Robotic Process Automation (RPA), automating interactions with legacy software that lacks APIs.
- Axiom.ai: Browser automation tool that lets you record actions (like clicks and typing) to automate web tasks without code.
2. Skills You Build Through Automation
Learning these tools isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about developing a modern technical mindset.
Systems Thinking
The ability to decompose a complex business process into a series of logical steps and triggers.
Logic & Boolean Algebra
Mastering filters, conditional branching (IF/ELSE), and wait-conditions to handle edge cases.
Data Architecture
Understanding how different apps structure data using JSON, Webhooks, and API keys.
AI Prompt Engineering
Learning to guide LLMs within a workflow to perform sentiment analysis or data extraction.
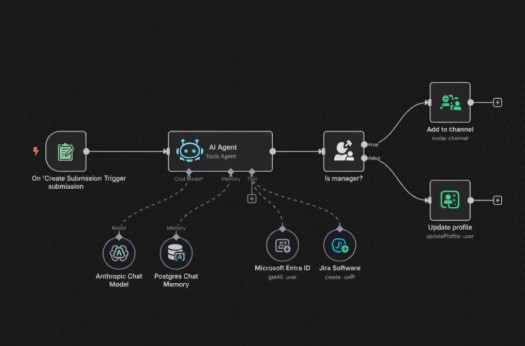
Figure: Automation Architecture Diagram
3. The 2026 Automation Roadmap
Phase 1: Identify “Friction Points”. Audit your week. Any task involving “copy-paste” or manual data entry is a candidate.
Phase 2: Standardize the Input. Automation fails on messy data. Create forms (Typeform/Google Forms) to ensure inputs are consistent.
Phase 3: The MVP (Minimum Viable Process). Build a single-trigger automation first (e.g., Save Email Attachment to Folder).
Phase 4: Error Handling & Scaling. Add notifications for when an automation fails so you can fix it before it impacts your work.
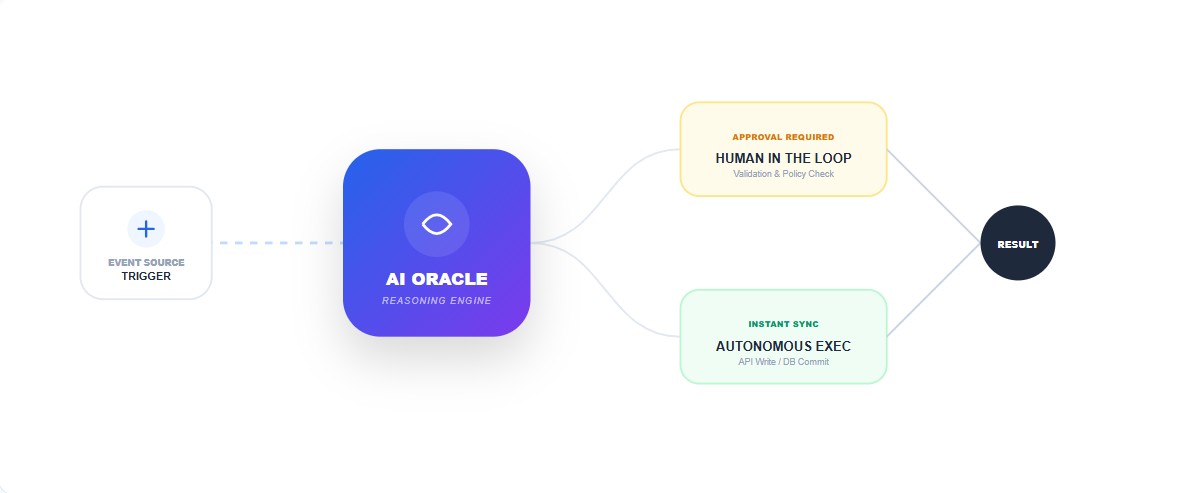
Figure 2.0: Optimized Process Flow Visualization
4. Comprehensive Comparison Table
| Tool | Primary Use | Complexity | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zapier | Simple Integrations | Beginner | Largest App Ecosystem |
| Make | Complex Data Flow | Intermediate | Visual Logic Mapping |
| Power Automate | Enterprise Workflows | Intermediate | M365 Native Integration |
| n8n | Custom/Hosted Logic | Advanced | Coding Flexibility |
| Axiom.ai | Browser Bot / Scraping | Intermediate | No-API Automation |